By Rudra Srinivas
Ever since IBM’s John Patrick coined the term ‘Ethical Hacking’ in 1995, the profession has grown to become a much-needed aspect in security programs. The growing popularity of certification courses on ethical hacking and bug bounty programs illustrates the importance of ethical hackers for today’s businesses.
But still, the term ‘Ethical Hacker’ conflicts with the image of hackers, which is portrayed as cybercriminals. Apart from data security personnel and government regulators, most people might not be familiar with ethical hacking. A look at the history of some notable ethical hackers possibly mitigates the negative connotations around it. Below are some of the famous ethical hackers around the world:
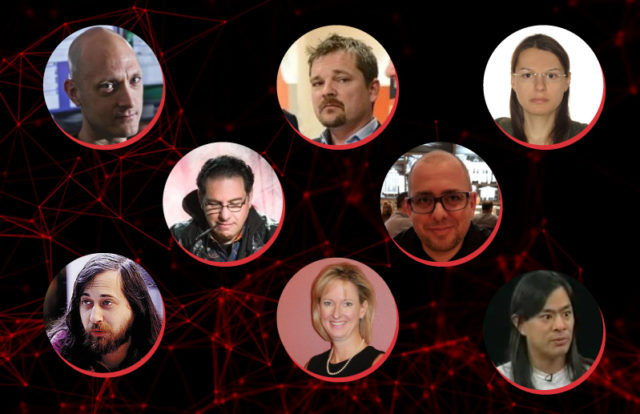
Kevin Mitnick
Kevin Mitnick is an American computer security consultant, author, and a black hat turned white hat hacker. He’s best known for his high-profile arrest in 1995 by the FBI for his various black hat escapades. Kevin Mitnick was an inveterate hacker since he was 13, using his social engineering skills to trick people into giving up passwords and other security information. His black hat escapades included stealing software from DEC systems and obtaining unauthorized access into Pacific Bell voice mail computers. He holds the distinction of being the first hacker to make the FBI’s Most Wanted list, but he’s now using his skills to do good. Kevin Mitnick is now a trusted security consultant helping consumers protect their information against threats. He also runs his computer security consultancy firm, Mitnick Security Consulting LLC.
Tsutomu Shimomura
Tsutomu Shimomura is a cybersecurity expert, physicist, and is credited with tracking down Kevin Mitnick. Being a computational physics research scientist, Shimomura also worked for the National Security Agency (NSA). He was known to be one of the leading researchers who raised awareness of the lacking security and privacy of cellular phones at that time. The founder of Neofocal Systems used his security skills for ethical purposes and played a key role in bringing Kevin Mitnick to justice. His book Takedown was later adapted to a film called Track Down.
Richard Stallman
Richard Stallman is an American free software movement activist, software developer, noted hacker, and founder of the GNU Project. Stallman was a programmer at MIT’s Artificial Intelligence Labs, where he constantly engaged in hacking activities. The creative computer programmer who strongly believed in freely modifying and sharing computer codes left MIT over concerns about software copyright rules.
According to him, a hacker means someone who enjoys playful cleverness. Stallman invented the concept of Copyleft, a legal mechanism that allows all programmers to use, modify, and redistribute a program’s code.
Charlie Miller
Charlie Miller, a security researcher, is best known for exposing vulnerabilities in Apple products. His most famous white hat achievements include discovering a critical MacBook Air bug at a Pwn2Own contest in 2008, from which he pocketed a $10,000 prize, beating the Safari security system in 2009, and finding security flaws in Apple’s iPhone and iPad.
Miller worked for the National Security Agency for five years as a computer hacker. He then worked for Twitter’s information security team as well as the autonomous vehicle security team at Uber. He currently works as a security researcher for Cruise Automation.
Greg Hoglund
Greg Hoglund is a specialist in computer forensics who worked with the U.S. Government and the Intelligence Community, providing his white hat capabilities to the pursuit of justice. He’s best known for his work in physical memory forensics, attribution of hackers, and malware detection.
In 2003, Hoglund founded HBGary, a company focussed on security, which later joined the McAfee Security Innovation Alliance in 2008. He also founded multiple security companies and is a frequent speaker at computer security conferences like Blackhat, DefCon, Infosec, and SANS in the U.S., EU, and Asia.
Joanna Rutkowska
Joanna Rutkowska is a computer security expert and the founder of Qubes OS, a security-focused desktop operating system. She’s best known for her research on low-level security and stealth malware. Rutkowska became known after she presented the vulnerabilities in the Vista kernel at the Black Hat conference in Las Vegas in August 2006.
Her fame as a whitehat hacker grew after she exposed numerous attacks on virtualization systems and Intel security technologies, including the famous series of exploits against the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (TXT). Her skills earned many invitations to speak at prominent conferences like RSA, RISK, Black Hat, the Gartner IT Security Summit, and others.
Sherri Sparks
Like Joanna Rutkowska, Sherri Sparks is a security researcher and made rootkits and stealth malware her pursuit. Sparks is the President of Clear Hat Consulting, specialized in Windows kernel and hypervisor development, which she co-founded in 2007 along with Shawn Embleto.
Her ethical hacking skills became known after she exposed how operating system-independent rootkits, such as the proof-of-concept System Management Mode-based rootkit she built could be used to compromise computer networks at Black Hat Conference 2008. She has given various demonstrations at RSA, Black Hat, and other IT security summits on her research interests which include offensive, defensive stealth code technologies, and digital forensics.
Marc Maiffret
A high school dropout, once the bad boy in a hacking group called Rhino9. After being raided by the FBI at the age of 17, Marc Maiffret realized that his hacking skills could be used for good.
He started his new beginning by co-founding security software company eEye Digital Security, which was credited for exposing vulnerabilities in Microsoft products such as the Code Red worm. The renowned security researcher and entrepreneur went on to create vulnerability management products and web application firewall products, which have been recognized with numerous awards.
“For much of my career I’ve had an opportunity to help technology vendors stay ahead of the bad guys through vulnerability research that identified potential weaknesses in the IT infrastructure before they could be maliciously exploited,” said Maiffret.
Maiffret served as Chief Technology Officer at vulnerability management firm BeyondTrust, which acquired eEye Digital Security. He also served as a Chief Security Architect at anti-malware firm FireEye. In 2015, Maiffret left BeyondTrust to embark his second security venture.
Rudra is part of the editorial team at CISO MAG and writes on cybersecurity trends and news features.